What is Merkle Tree?
Merkle Tree is also called as a Binary Hash tree, a type of data structure used for the large set of data. Merkle tree is used where the data required being efficiently summarized and verification of data integrity.
It provides critical features necessary for Blockchain Network.
- Compress large data set, it removes any superfluous branches and keeping only the ones needed for establishing the proof.
- It has the ability to verify which transaction is included in the block.
- Its light weighted, as the entire chain doesn’t needs to be downloaded for each and every transaction
Overall performance and scalability.
A complete merkle tree looks like the below diagram.
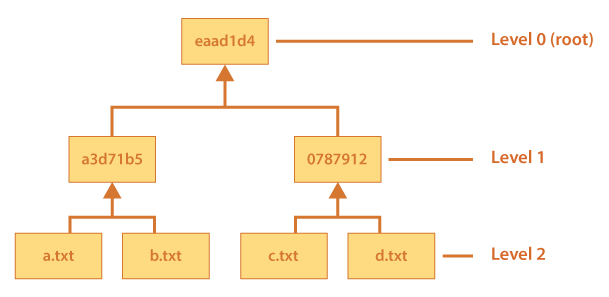
In Level 2 of the above structure, “a.txt”, “b.txt”, “c.txt” and “d.txt” is the leaf node of the merkle tree and each leaf node is the hash of the block data. Level 1 is a hash combination of two child node pair thus parent hash “a3d71b5” is combination of (Hash of a.txt + hash of b.txt). Likewise, Parent hash “0787912” is combination of (hash of c.txt + hash of d.txt) and so on. Level2 is the root which is combination of the hashes of “a3d71b5” + “0787912”. In this manner there can be N number of levels in the binary tree with each node having either 0 or 1 or 2 children. However, the root is a single hash of its two immediate children node pair
Merkle tree within Blockchain
Merkle tree is used inside the block of the Blockchain to represent all the transactions within that block. Thus, the block content can be validated using single string of fixed length and their by eliminating the need to store individual transactions.
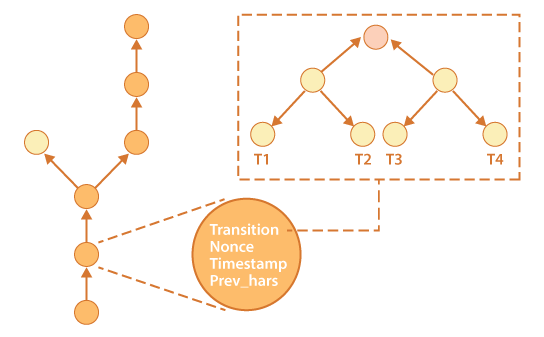
A continuously growing block of records where each block is linked to its successor block securely via cryptography is nothing but a Blockchain.
Now each block contains hash pointer of its previous block, the current timestamp and the transaction data in hash format. The data once stored within the block cannot be deleted or changed. For any changes it creates an altogether a new block which gets linked to the future chain. The transaction data are usually stored in the leaf node of the merkle tree. The root hash is then stored in the block thus creating the tree structure. So each block in the blockchain hold hash transactions and are encoded into a merkle tree.
When we say that each block is a permanent block within the Blockchain i.e. it neither can be deleted nor modified. For example supposes anyone who wants to change or modify the data within a current block in the blockchain. If they manage to manipulate the data somehow, then they have to change the hash of its previous block so that it points correctly to the modified block.
Changing the hash of its previous block would also mean to change the hash of its previous to previous to block, so that it remains in the same structure tree. Likewise in order to have the tree structure valid, the entire block hashes needs to change which are connected to each other. It has to traverse all the way to root in order to change a single block. And in distributed ledger it will become virtually impossible since in distributed network there is continuous consensus to verify any transaction that is being added to block within the blockchain.
Thus, blockchain is tampered proof free; hence making it’s the most secure structure for any transactions.
Merkle tree testing can be accomplished by verifying the hashes of a block and state root for each level. At Magic BlockchainQA, we are helping the global FinTech companies to test and implement their Blockchain model successfully. Our highly skilled Blockchain QA team offer end to end product testing on Blockchain network and smart contracts. With in-depth domain understanding, can help in automating the regression test bed for easy and production-ready solution.
To know more about our FinTech focused BlockChain please contact us at info@magicblockchainqa.com.